Do your hips protrude far back, does your stomach protrude beyond the tip of your nose - and does your back ache when you bend forward? Then you could have a hollow back. This particular form of spinal curvature doesn't just affect pregnant women or "beer bellies": the root of the problem often lies in incorrect posture caused by tense muscles.
But a hollow back is not set in stone! With the right exercises and tips, you can successfully counteract excessive curvature and walk through life upright.
We reveal the most important facts about your spine and show you simple exercises to train away your hollow back.
Content
2 Definition: What is a hollow back?
3. development of a hollow back
4. hollow back: symptoms and effects
5. treat a hollow back: Exercises and tips
6 Our conclusion on the hollow back
The anatomy of your spine
Before we familiarize you with the concept of a hollow back (hyperlordosis), we would like to introduce you to the basics of your spine - because this background knowledge will help you to understand what a hollow back is all about.
In principle, a healthy spine is never completely straight. Perhaps you have heard of the so-called"S-shape" in this context? This term comes from the fact that the sections of your spine are curved twice in the shape of the letter S:
The first forward bend is in the six vertebral prominences of the cervical spine (C-spine). At the level of the thoracic spine (thoracic spine), the opposite bend occurs backward. Along the lumbar spine (LS) toward the pelvis, the spine curves forward again and ends in a steep curve pointing backward toward the sacrum and coccyx.
But why all this up and down? The double S-shape developed in the course of human evolution as an adaptation to the upright gait. The center of gravity of our body had to be shifted towards the pelvis in order to maintain balance. This initially led to a forward curvature of the spine between the sacrum and lumbar spine. However, the change resulted in a posture that caused our ancestors' upper bodies to lean backwards. This resulted in a second curve between the cervical and thoracic spine, which made it easier to carry the head. Voilà - the double S-shape was born, with the added benefit that our spine could naturally absorb shocks and keep our movements smooth and stable.
Definition: What is a hollow back?
As you now know, our spine has natural curves. A curvature towards the back is called kyphosis and a curvature towards the front is called lordosis.
With a hunched back, for example, the curvature of the thoracic spine is increased, which is why this phenomenon is referred to as hyperkyphosis. Accordingly, the medical term for a hollow back is hyperlordosis: with this poor posture, the lower half of the body moves forward, causing the lumbar spine to curve more and the pelvis to tilt forward. As a result, the abdomen forms a bulge and the body's center of gravity changes. To maintain balance, the thoracic spine tilts backwards and the shoulders pull back so that the rib cage lies behind the central body axis. The result is a visible hollow in the back, which gives the hollow back its name.
Good to know: A hollow back can also be accompanied by a hunchback. This phenomenon is called a hollow hunchback.
Development of a hollow back
A hollow back usually develops due to genetic factors, as a result of illness or due to learned causes such as too little exercise, poor posture or a relaxed posture during pregnancy. However, it is often difficult to clearly differentiate the exact causes - especially if the hollow back develops due to a disease such as an underactive thyroid in combination with obesity.
In most cases, tense and shortened muscles contribute significantly to the formation of a hollow back. These are learned in childhood and intensified over the years.
Genetic causes of a hollow back
The extent to which a person develops lordosis depends, among other things, on their ethnic origin. Among the Pygmies, an ethnic group from Africa, a hollow back is commonplace - because it is passed down from generation to generation. It is therefore not a consequence of illness or poor posture, but can be seen as a completely normal curvature of the spine.
Hollow back due to diseases
In addition to obesity, diseases such as spondylolisthesis (slipped vertebrae) or Pomarino's disease (toe walking) can lead to a hollow back. In the case of slipped vertebrae, individual vertebrae slide against each other, can shift forwards or backwards and promote hyperlordosis.
Lack of exercise, tense muscles, incorrect posture
One of the most common causes of a hollow back is our everyday life:
The modern way of life is characterized by sitting - in the office, in the car, on the bus, at school, on the couch. These one-sided strains and lack of movement take their toll on muscles, fascia and the like. The muscles of the so-called hip flexors play a particularly important role in a hollow back. They extend from the lower spine and pelvis to the inside of the thighs and form the only muscular connection between the upper and lower body.
When sitting, the hip flexors and your abdominal muscles are in a shorter position than the back and hip extensors on the back of your body, which you need primarily for standing up and standing. If you spend a large part of your day sitting on a chair, these muscles and fasciae shorten or build up tension and become rigid over time. This leads to a muscular imbalance, your muscles pull on your spine from the front and back and your lumbar spine is pulled "into a hollow back".
Hollow back: symptoms and effects
In contrast to evolutionary adaptation, a "trained" hollow back due to poor posture, lack of exercise or tense muscles offers no benefit to your body. In fact, in addition to the somewhat unattractive appearance, it can also cause pain, restricted mobility and other complaints.
The main symptom of hyperlordosis is back pain associated with lumbar spine syndrome. The vertebrae can slip out of place, which can result in wear and tear of the intervertebral discs and a herniated disc. A hollow back often causes tingling and numbness when the tension in the back muscles presses on the sciatic nerve. People with a hollow back can also experience pain when bending the upper body or lifting objects.
Treat hollow back: Exercises and tips
Is your hollow back causing you pain? Then it's high time to do something about it! Whether acupressure or exercises against hollow back: In the following, we give you helpful tips to relax your muscles, restore the balance in your back and prevent pain in the long term.
The 3 best exercises against a hollow back
With our self-help exercises, you can train away your hollow back, free yourself from muscular tension and relieve back pain and other symptoms of hyperlordosis.
Exercise 1: Stretch hip flexors - beginner
For this exercise, get into the quadruped position. Your hands are on the floor and point outward at a 45-degree angle. Tighten your abdominal muscles and maintain this tension while slowly moving your upper body forward. Let your hips sag between your fully extended arms so that your thighs touch the floor. Your abdomen will remain tense and you will feel a stretch in your groin as well as your back. Hold the position for about 2 minutes if you can tolerate the stretching pain from the hollow back.
Keep in mind that if your hip flexors are severely shortened, your thighs may not touch the floor and you may not be able to fully relax your hips. However, with continued practice, you will find that you can gradually move your upper body into the desired position and counteract the muscular shortening even more effectively.
Exercise 2: Stretch hip flexors - advanced
Assume the starting position from hollow back exercise 1 including abdominal tension (!). Angle your left leg by placing the foot against the knee of your right, extended leg. The left leg will tilt slightly to the side, causing you to notice an intense stretch in the right hip and pelvis area. Slowly lower yourself into the position. After one minute, switch sides and remain in this position for another 60 seconds.
Exercise 3: Stretch hip and back extensors
Sit on the floor and stretch your legs out in front of you. Bring the soles of your feet together so that your legs are bent and your knees fall to the side. In the next step, bend forward and clasp the tips of your feet with your hands. Bend your legs a little more if this makes it easier for you to reach your feet. While keeping your feet clasped, bend your upper body deeper and deeper forwards until you feel a stretch in your lower back. This is where your hollow back is! Stay in this stretch for around 2 minutes - always taking your personal pain threshold into account, of course.
How long does it take to get rid of a hollow back?
The time you need to correct a hollow back depends, among other things, on the severity of the hyperlordosis, your physical fitness and the regularity with which the exercises are performed. As a rule, you will achieve an improvement in several weeks or months with consistent stretching exercises and muscle relaxation techniques - provided the hollow back is not caused by significant structural changes in your spine.
What to do about the hollow back - tips for everyday life
As you already know, a sedentary lifestyle with one-sided posture is one of the main causes of a hollow back. For this reason, the best prevention lies in adapting your daily actions - for example, by integrating a combination of regular exercise, a healthy diet and conscious posture correction into your life.
-
Tip 1: Exercises
Targeted stretching of your muscles helps you to avoid a hollow back. In addition to our three favorite exercises, yoga and Pilates are also suitable for keeping your body supple and flexible. -
Tip 2: Posture
Pay attention to your posture throughout the day - especially if you are sitting or standing for long periods. Try to regularly pull your shoulders back and push your chest out to achieve a beneficial spinal position. -
Tip 3: Healthy eating
Being overweight can put additional pressure on your spine and lower back muscles and increase a hollow back. A healthy, balanced diet and regular exercise can help you manage your weight in the long term. -
Tip 4: Hard or soft mattress for a hollow back?
The choice of the right mattress is very individual and depends on your preferred sleeping position and your body weight. However, a medium-firm mattress seems to offer the ideal compromise for a hollow back: It has enough stability to keep the spine in a neutral curve and enough comfort to avoid pressure points. -
Tip 5: Sitting and sleeping positions
Avoid spending long periods of time in a position that reinforces your hollow back. When sitting, use a lumbar support to keep your lower back in its natural shape. When sleeping, you can place a Pillow under or between your knees to support the alignment of your hips and spine. -
Tip 6: Massage and acupressure
Massages and acupressure are very effective for muscle tension caused by a hollow back. Opt for massages that target the lower back and hips. Acupressure, for example using an acupressure mat, can also promote blood circulation and relaxation of tense muscles.
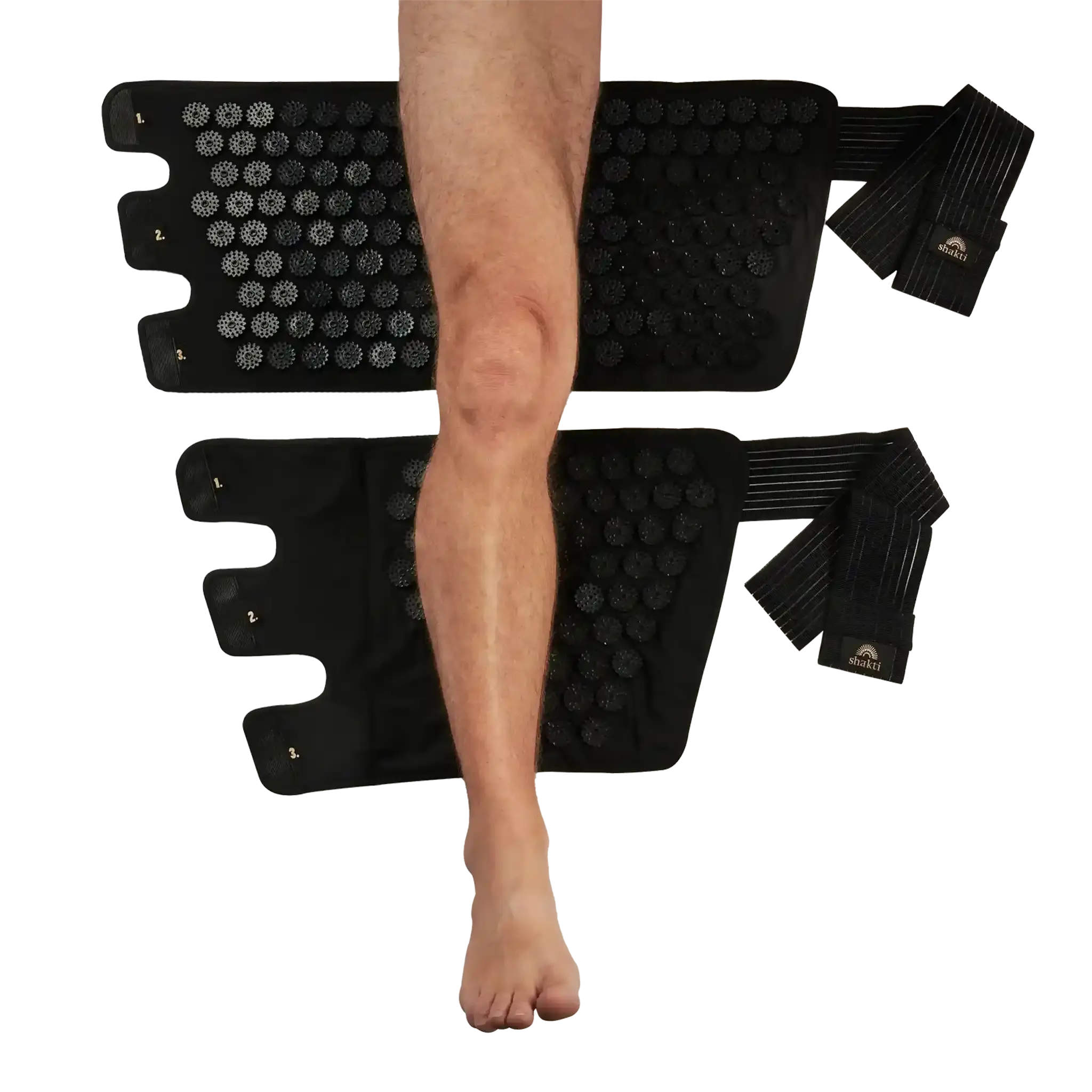
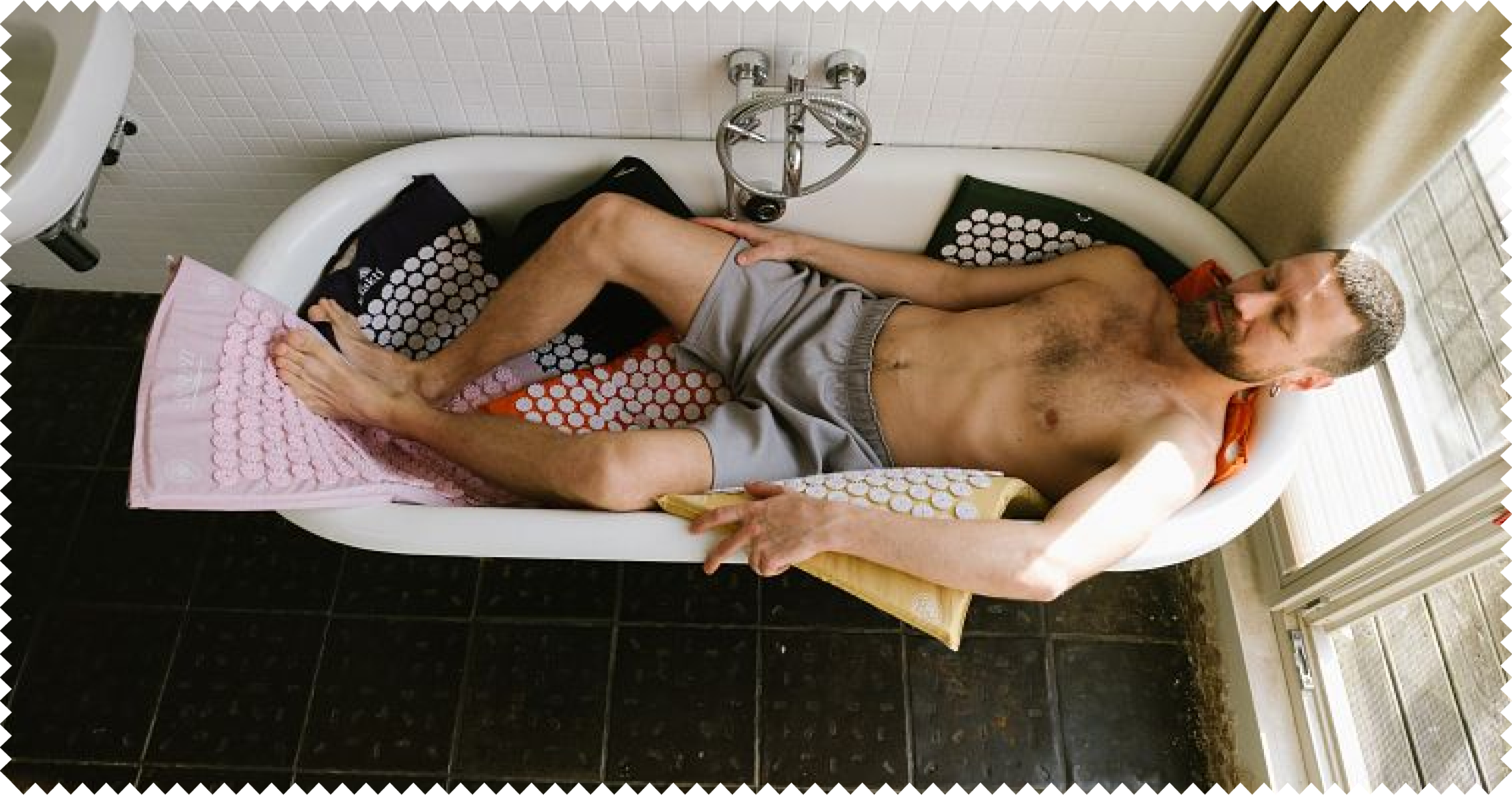
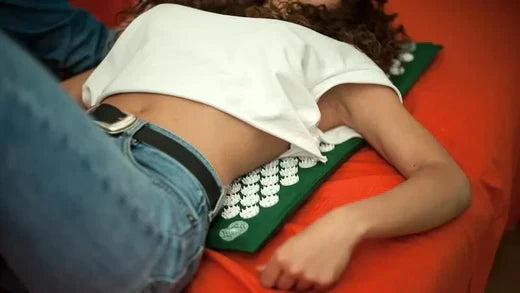
Release muscular tension with acupressure
An acupressure mat can be used for a hollow back to relieve muscular tension.
It works on the principle of acupressure - a traditional Chinese medical method that improves the flow of energy and relieves pain or tension by stimulating certain points on the body.
Position your mat on a flat and comfortable surface and gently lie down with your back on it. Come to rest and breathe deeply and evenly. Meditation music in the background or essential oils can also help you relax.
If it works for you, spend at least 20 minutes on the mat and use it regularly for optimal results and to reduce the symptoms of your hollow back.
Our conclusion on the hollow back
As a common posture problem, a hollow back can cause unpleasant symptoms such as back pain or restricted movement. Since hyperlordosis is caused not only by genetic or disease-related factors, but also by your posture and an unbalanced lifestyle, it is important to consciously shape your everyday life: Do regular hollow back exercises, pay attention to your posture, choose a suitable mattress and use relaxation techniques or acupressure to stop the hollow back. With a little perseverance, patience and discipline, you can sustainably increase your well-being and improve your quality of life.
With this in mind: be active, stay flexible and give your back the rest it deserves!