Who hasn't been there? You go to the doctor, describe your symptoms, have yourself examined and in the end you are told that it is due to stress. Of course, there is often more to it when we feel unwell, but stress in particular can have a negative impact on almost every aspect of our health. There is hardly a person who does not feel stressed from time to time or even regularly. While occasional tension is completely normal and cannot be avoided, a prolonged or frequent feeling of stress is something that should be tackled - because in the worst case scenario, mental and physical illnesses can develop or their symptoms worsen as a result of permanent overload, which already significantly restricts the quality of life. So today we are asking ourselves: what is stress, what triggers it and what can we do about it?
Content
1st interview with neurologist & Ayurveda expert Dr. Nadine Webering
2. possible symptoms of stress
3. consequences of stress: long-term effects on the mind & body
4. stress management: What helps against stress?
5. how to combat stress in everyday working life
6. conclusion: recognize & combat stress
What is stress anyway?
Stress is an everyday topic of great importance, as we encounter it in all possible areas of life. We make a fundamental distinction between positive and negative stress. "Positive stress"(eustress) may sound contradictory at first, but it can actually have beneficial effects - such as increasing motivation and performance. These selective stress reactions occur, for example, when you are looking forward to the birth of a child or when starting a new job. It increases alertness and performance and often also stimulates action. As soon as the respective situation has occurred or passed, the eustress automatically decreases again and we can "take a deep breath" again.
This contrasts with dysstress or disstress, which can have serious physical and psychological consequences if it persists. From adrenaline rushes in acute dangerous situations to long-term health problems caused by chronic stress - our body and mind react to stressors in many different ways. Disstress is generally perceived as negative and burdensome and usually arises in connection with unpleasant or even threatening situations - for example, job loss, health problems and divorce. If disstress is not counteracted by suitable coping mechanisms, it can turn into feelings such as anxiety, anger and frustration in the long term. Another reason for disstress: in dangerous situations that require immediate reactions, such as sudden loud noises or rapidly changing light, the body reacts instinctively. However, if such stressors are constantly present, the body continuously releases stress hormones. These hormones, including neuropeptides such as substance P and opioid peptides, contribute to the maintenance of tension and can lead to long-term problems such as nervousness and exhaustion.
What triggers are there?
The triggers of stress can basically be divided into two categories:
- Psychosocial stressors: Financial worries, social isolation, complicated working relationships, relationship conflicts - all these factors are potential stressors and can have a significant impact on our mental as well as physical well-being.
- Abiotic stressors: Environmental conditions such as extreme temperatures, noise and intense sunlight can also trigger stress. Unfortunately, these factors in particular cannot usually be (completely) avoided.
Stress is basically a natural reaction of the body to challenges and can behealthy and beneficial in moderation . In moderate doses, it helps you to perform better and develop new skills. However, once the stress becomes chronic, it can lead to serious health problems.
Possible symptoms of stress
Recognizing the symptoms of disstress (or eustress) is sometimes not so easy - because they manifest themselves in many different ways and can affect almost all aspects of our physical and mental health.
One of the most common physical symptoms of acute stress is an increased heart rate, which is accompanied by an accelerated heartbeat and rising blood pressure. At the same time, the breathing rate increases, which results in rapid breathing and often sweaty hands. These physical reactions are part of the so-called "fight-or-flight" mechanism, which prepares the body for potential danger. Muscle tension increases, so that stress often leads to headaches and tension .Back pain caused by stress, as well as flickering eyes, ringing in the ears and other physical reactions are therefore not uncommon . The body ensures that the muscles are optimally supplied with oxygen and nutrients in order to be able to react quickly to danger. The release of neurotransmitters and hormones plays a key role in this, as they contribute to the increased tension. Stress can even cause gray hair.
Among other things, the tension also affects the digestive system . The functions of the digestive and reproductive systems are reduced in order to save resources for vital processes. This can lead to a variety of problems, including loss of appetite, indigestion and other physical symptoms such as nausea, muscle weakness, skin problems, joint pain and increased sweating. Stress can also trigger tinnitus . A weakened immune system is a common consequence of prolonged stress, which increases susceptibility to infections.
Psychological symptoms are just as varied and range from emotional fluctuations such as sadness and anger to anxiety and depression. Concentration problems and irritability are common side effects, as are sleep disorders and social withdrawal. Children often show specific symptoms of psychological stress such as fear of the dark, eating disorders and school anxiety.
These are some of the most common symptoms; however, there are many other ways in which disstress can manifest itself. The symptoms vary from person to person and always depend on the cause.
Consequences of stress: long-term effects on the mind & body
In the long term, stress can cause a variety of health problems that go beyond short-term complaints. Acute tension affects both the muscular and circulatory systems as well as central decision-making processes. However, prolonged stress can affect the entire organism.
Consequences for metabolism and immune system
One of the most serious consequences of chronic stress is the impairment of the metabolism and the immune system. This weakening of the immune system increases susceptibility to infections and other illnesses - such as cardiovascular diseases like high blood pressure, coronary heart disease and heart attacks. In addition, digestive problems, muscular tension and general physical tension can occur, which significantly impairs quality of life.
Psychological effects and professional consequences
Mental health problems are another significant risk. Chronic stress can lead to depression, anxiety and other mental disorders. Professional and social functioning is severely impaired, which can of course have a number of consequences - such as high levels of sickness absence and social isolation, which in turn exacerbates the problem.
Long-term increase in cortisol
Among other things, cortisol is known as the "stress hormone". A permanent state of stress increases the level of cortisol in the blood, which can lead to a variety of problems. Long-term elevated cortisol levels are known to exacerbate cardiovascular problems, impair insulin action and thus increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. It also changes the distribution of fat in the body, which can lead to overweight and obesity.
Influencing behavior
Chronic stress also influences behavior and lifestyle. People under high stress often tend to adopt unhealthy coping strategies such as smoking, alcohol consumption and an unbalanced diet. Lack of exercise and sleep disorders are other behaviors that are exacerbated by the constant tension.
Physical complaints and sensory disorders
The lack of rest breaks and prolonged stress also increase the body's general level of arousal. Physical complaints such as chronic muscle tension, headaches and back pain are often the result. Some people even develop sensory disorders such as hearing problems or impaired vision.
Extreme cases and severe mental disorders
In extreme cases, chronic stress can lead to serious mental disorders, including burnout, panic attacks and phobic disorders. A feeling of exhaustion, both physical and psychological, characterizes the lives of those affected and significantly impairs their well-being. In such cases, treatment by specialists - such as therapists or psychiatrists - usually becomes essential.
Coping with stress: What helps against stress?
Different approaches are needed to effectively manage stress, taking into account both physical and psychological aspects. There is no miracle cure or one-size-fits-all solution, as everyone deals with stressful situations and tension differently and reacts differently to different coping methods. However, there are some methods that have stood the test of time and also some factors that you should consider in order to counteract tension in the best possible way.
Relaxation techniques
Relaxation techniques such as progressive muscle relaxation are a proven way to reduce stress and offer numerous benefits. This method helps to reduce muscle tension and cope better with stress-related symptoms such as headaches and tension.
Meditation in its many forms, including mindfulness meditation and transcendental meditation, has also been shown to be extremely effective. Regular meditation practice can lower cortisol levels, improve overall well-being and increase stress resilience.
Nutrition & sleep
Nutrition and sleep are additional factors that are often overlooked but have a huge impact on stress levels. A balanced diet, rich in vitamins and minerals, can strengthen physical resilience and keep energy levels stable.
Sufficient and high-quality sleep is essential for the regeneration of the body and the reduction of stress hormones. You should get eight hours of sleep so that your body and mind can recover sufficiently from the stresses and strains of everyday life.
Leisure activities
Walks in nature, creative hobbies or simply reading a good book can also provide you with valuable services. Fill your everyday life with leisure activities that you enjoy without putting yourself under pressure.
Exercise therapy also shows remarkable effects. Sports such as yoga, running or swimming not only promote physical fitness, but also release endorphins, which improve mood and reduce stress.
Further methods & approaches
- Time management: Effective time management helps to identify and minimize stressors. Setting clear priorities and organizing the daily routine reduce unnecessary stress and create space for relaxation.
- Avoid stress: Identifying and avoiding stressors is also crucial. Factors such as excessive demands on oneself, constant availability or unhealthy working conditions can be reduced through targeted measures.
- Professional support: You don't always have to cope with everything on your own. Seeking professional help is by no means a sign of weakness. It is advisable to seek help from your family doctor or a therapist, especially if you are under prolonged stress.
- Cognitive restructuring techniques: These can help to gain a new perspective on stressful situations. This can change inner attitudes and ways of thinking that increase tension.
- Letting go of perfectionism: Changes in personal attitude also contribute to stress reduction. If such stress-increasing factors are recognized and modified, everyday stress can be better managed.
How to combat stress in everyday working life:
Some love their job, others not so much. But one thing applies equally to everyone: Our job is a frequent cause of stress. Deadlines have to be met, next week's meeting with the boss is a cause for concern and there may even be conflicts between employees - it's almost impossible to avoid tension. But there are a few things that can help:
- Regular breaks and relaxation exercises during working hours promote recovery and increase productivity. Techniques such as the Pomodoro technique, which involves taking a short break after 25 minutes of work, can help to increase concentration and reduce tension. Switching between different work tasks can also help to reduce monotonous and tiring activities.
- Effective time management is another important factor. Prioritizing tasks and delegating less important activities reduces the workload and creates space for creative and challenging projects. It is helpful to formulate clear goals and create realistic schedules in order to avoid excessive demands.
- A constructive approach to conflicts in the working environment is also crucial. Regular feedback meetings and an open communication style create a healthy working atmosphere and help to reduce the potential for stress.
- Cognitive techniques can be used to reduce negative evaluations of stressful situations. This includes mindfulness and resilience training as well as special stress management seminars that teach individual coping strategies. Through such approaches, professionals can change their assessment of stressful situations and deal with stress more effectively.
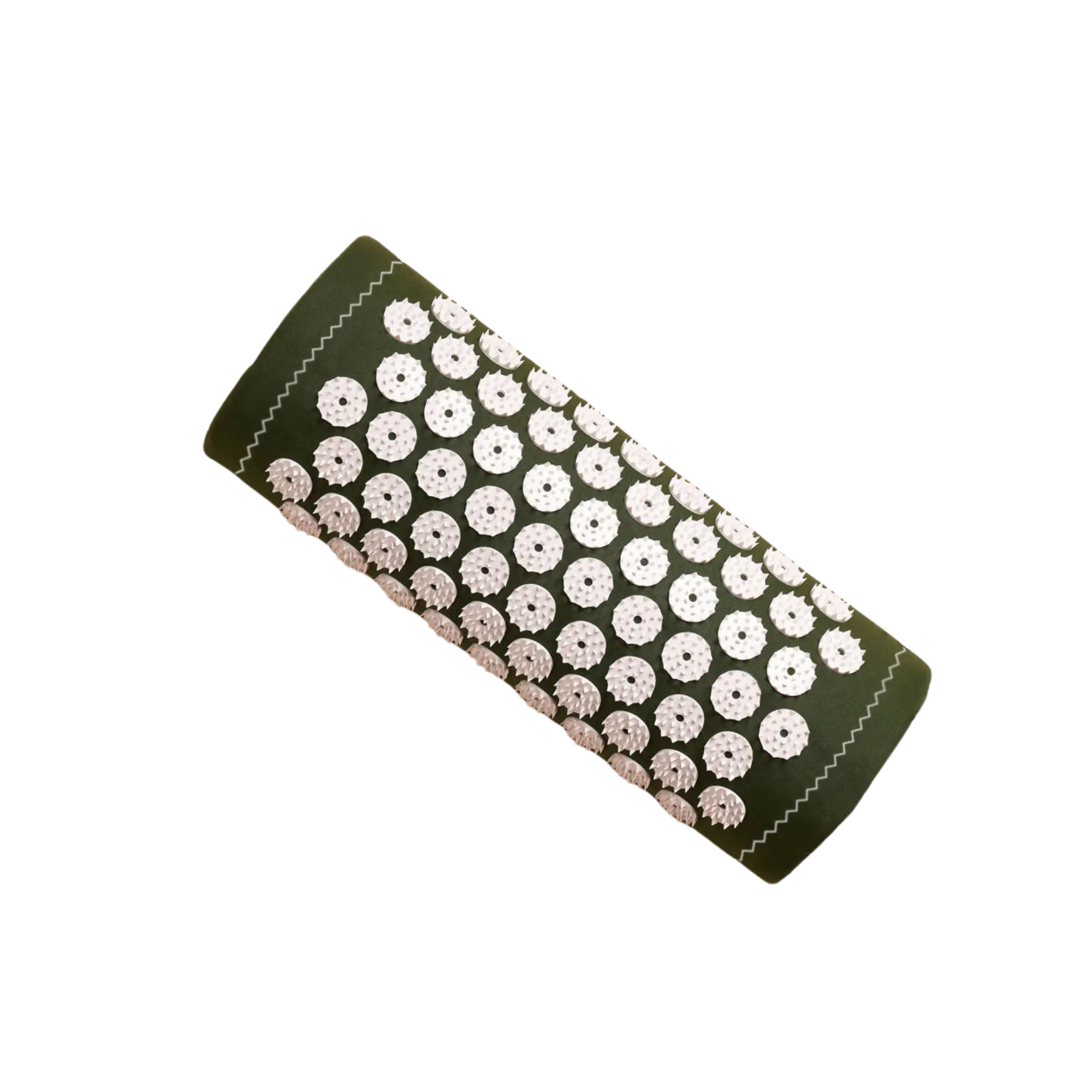
Acupressure against stress
Acupressure is an alternative form of therapy based on traditional Chinese medicine and is gaining increasing attention as a method of stress management. The aim of this technique is to release energy blockages by applying pressure to certain points on the body, thereby restoring balance in the body. There are also certain acupressure points that should be given particular attention in times of stress.
Acupressure can be applied in various ways. For example, use an acupressure mat to reach as many acupressure points as possible. If you suffer from symptoms such as headaches or tension in the neck area due to the tension, we also recommend an acupressure cushion that specifically targets this area.
Some studies show that the regular use of acupressure can lower the heart rate and increase general well-being. In combination with other relaxation techniques such as meditation or yoga, acupressure can therefore play an important role in coping with stress.
Conclusion: Recognizing & combating stress
We now know that there are different types of stress, which can be caused by a range of different triggers. While eustress can even have positive effects, disstress has a negative impact on our physical and mental health. This negative stress can have serious health consequences, especially if it lasts for a long time. It is therefore important to counteract the tension - for example by changing your diet, getting enough exercise, using relaxation methods or sessions on your Shakti Mat. Meditation and yoga can also help to relieve tension and thus improve your general well-being. However, if your stress levels are particularly high or persistent, we strongly recommend that you seek professional help.